Usage¶
Command Line Interface¶
Command structure:
explorepy <command> [args]
Available Commands¶
find_device Scans for nearby explore-devices. Prints out Name and MAC address of the found devices.
acquire Connects to device, needs either MAC or Name of the desired device as input.
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. “Explore_12AB”).
record_data Connects to a device and records ExG and orientation data into 2 separate files. Note that in CSV mode there will be an extra file for the marker events. In EDF mode, the data is actually recorded in BDF+ format (in 24-bit resolution).
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB). Note that either device name or MAC address is needed.-for--filenameThe prefix of the files.-tor--typeFile type (edf and csv types are supported currently).-owor--overwriteOverwrite already existing files with the same name (optional - the default mode is False).-dor--durationRecording duration in seconds
push2lsl Streams data to Lab Streaming Layer (LSL).
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB). Note that either device name or MAC address is needed.
bin2csv Takes a Binary file and converts it to 3 CSV files (ExG, orientation and marker files)
-ior--inputfileName of the input file-owor--overwriteOverwrite already existing files with the same name.
Note
For devices with firmware version 2.1.1 and lower, explorepy v0.5.0 has to be used to convert binary files.
bin2edf Takes a Binary file and converts it to 2 EDF files (ExG and orientation - markers will be written in ExG file). The data is actually recorded in BDF+ format (in 24-bit resolution).
-ior--inputfileName of the input file-owor--overwriteOverwrite already existing files with the same name.
Note
For devices with firmware version 2.1.1 and lower, explorepy v0.5.0 has to be used to convert binary files.
visualize Visualizes real-time data in a browser-based dashboard. Currently, Chrome is the supported browser. The visualization in IE and Edge might be very slow.
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB).-nfor--notchfreqFrequency of applied notch filter (By default, no notch filter is applied)-lfor--lowfreqLow cutoff frequency of bandpass filter (By default no bandpass filter is applied)-hfor--highfreqHigh cutoff frequency of bandpass filter (Both-lfand-hfmust be given if you want to apply a bandpass filter)-cfor--calibration_fileCalibration file name (e.g. “X_calibre_coef.csv”). If you pass this parameter, ORN module should be ACTIVE! To obtain this file refer to Explore.calibrate_orn module.
impedance Visualizes electrodes impedances in a browser-based dashboard. Currently, Chrome is the supported browser.
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB).-nfor--notchfreqFrequency of applied notch filter (By default, no notch filter is applied)
calibrate_orn Calibrate the orientation module of the specified device. After running this module, a file containing calibration data will be generated. Using this file, an extra computation block can be activated in the visualize to compute the physical orientation of the device from raw sensor data.
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB).-cfor--calibration_fileCalibration file name. If you pass this parameter, ORN module should be ACTIVE!-owor--overwriteOverwrite already existing files with the same name.
format_memory This command formats the memory of the specified Explore device.
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB).
set_sampling_rate This command sets the sampling rate of ExG on the specified Explore device. The only acceptable values for sampling rates are 250, 500 or 1000. Please note that this feature is in its alpha state. There might be some inconsistency with other modules in sampling rates except 250 Hz.
-aor--addressDevice MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).-nor--nameDevice name (e.g. Explore_12AB).-sror--sampling_rateSampling rate of ExG channels, it can be 250 or 500.
soft_reset
This command does a soft reset of the device. All the settings (e.g. sampling rate, channel mask) return to the default values.
* -a or --address Device MAC address (form XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX).
* -n or --name Device name (e.g. Explore_12AB).
Example commands:¶
Data acquisition: explorepy acquire -n Explore_XXXX #Put your device Bluetooth name
Record data: explorepy record_data -n Explore_XXXX -f test_file -t edf -ow
Push data to lsl: explorepy push2lsl -n Explore_XXXX
Convert a binary file to csv: explorepy bin2csv -i input_file.BIN
Convert a binary file to EDF and overwrite if files exist already: explorepy bin2edf -i input_file.BIN -ow
Visualize in real-time: explorepy visualize -n Explore_XXXX
Impedance measurement: explorepy impedance -n Explore_XXXX
Format the memory: explorepy format_memory -n Explore_XXXX
Set the sampling rate: explorepy set_sampling_rate -n Explore_XXXX -r 500
To see the full list of commands explorepy -h.
Initialization¶
Before starting a session, make sure your device is paired to your computer. The device will be shown under the following name: Explore_XXXX, with the last 4 characters being the last 4 hex numbers of the devices MAC adress
Make sure to initialize the Bluetooth connection before streaming using the following lines:
explore = explorepy.Explore()
explore.connect(device_name="Explore_XXXX") #Put your device Bluetooth name
Alternatively you can use the device’s MAC address:
explore.connect(device_addr="XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX")
If the device is not found it will raise an error.
Streaming¶
After connecting to the device you are able to stream data and print the data in the console.:
explore.acquire()
Recording¶
You can record data in realtime to EDF (BDF+) or CSV files:
explore.record_data(file_name='test', duration=120, file_type='csv')
This will record data in three separate files “test_ExG.csv”, “test_ORN.csv” and “test_marker.csv” which contain ExG, orientation data (accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer) and event markers respectively. The duration of the recording can be specified (in seconds). If you want to overwrite already existing files, change the line above:
explore.record_data(file_name='test', do_overwrite=True,file_type='csv', duration=120)
Visualization¶
It is possible to visualize real-time signal in a browser-based dashboard by the following code. Currently, Chrome is the supported browser. The visualization in IE and Edge might be very slow.:
explore.visualize(bp_freq=(1, 30), notch_freq=50)
Where bp_freq and notch_freq determine cut-off frequencies of bandpass filter and frequency of notch filter (either 50 or 60) respectively.
In the dashboard, you can set signal mode to EEG or ECG. EEG mode provides the spectral analysis plot of the signal. In ECG mode, the heart beats are detected and heart rate is estimated from RR-intervals.
EEG:
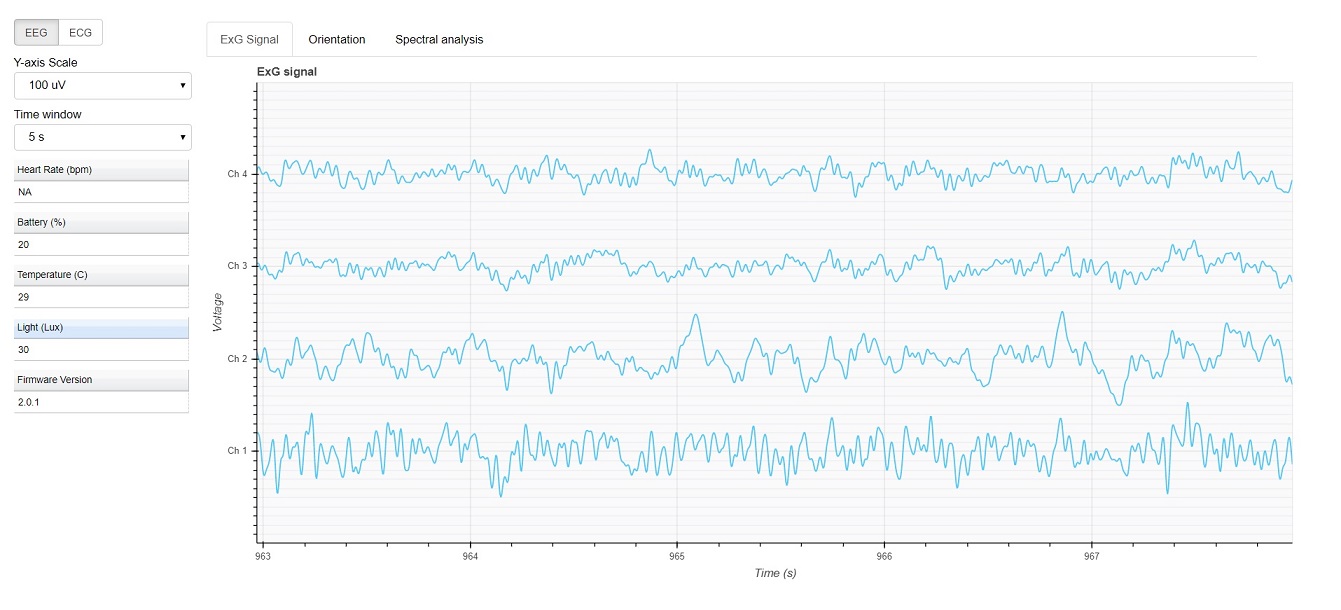
ECG with heart beat detection:
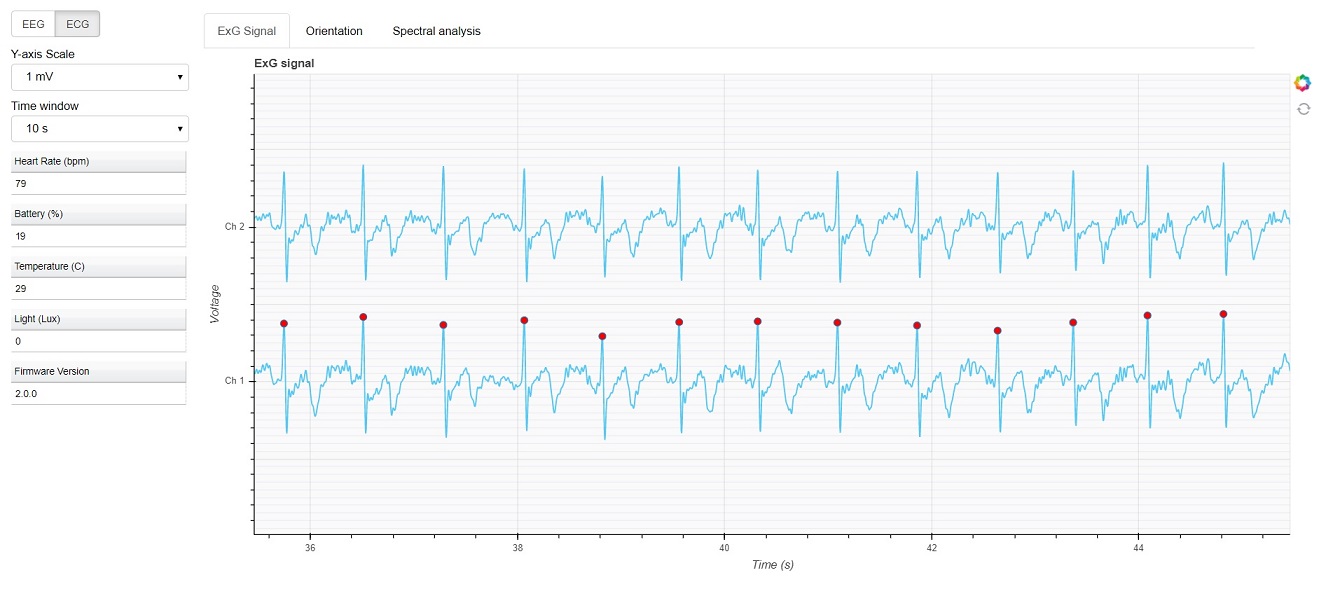
Impedance measurement¶
To measure electrodes impedances:
explore.impedance(notch_freq=50)
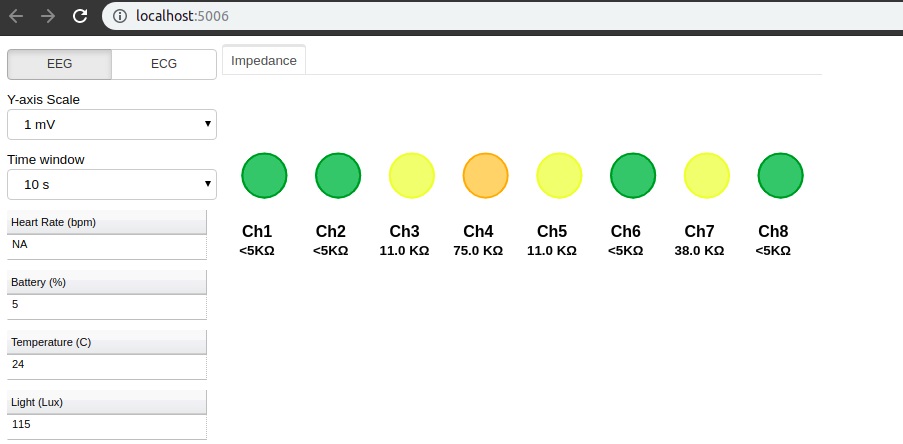
Note
The accuracy of measured impedances are subject to environmental conditions such as noise and temperature.
Labstreaminglayer (lsl)¶
You can push data directly to LSL using the following line:
explore.push2lsl()
After that you can stream data from other software such as OpenVibe or other programming languages such as MATLAB, Java, C++ and so on. (See labstreaminglayer, OpenVibe documentations for details). This function creates three LSL streams for ExG, Orientation and markers. In case of a disconnect (device loses connection), the program will try to reconnect automatically.
Converter¶
It is also possible to extract BIN files from the device via USB. To convert these to CSV, you can use the function bin2csv, which takes your desired BIN file and converts it to 2 CSV files (one for orientation, the other one for ExG data). Bluetooth connection is not necessary for conversion.
from explorepy.tools import bin2csv
bin2csv(bin_file)
If you want to overwrite existing files, use:
bin2csv(bin_file, do_overwrite=True)
Note
Currently, the binary files which the sampling rate or ADC mask are changed during recording are not supported. You can use python script and explorepy.Explore.record_data() function as an alternative.
Event markers¶
In addition to the marker event generated by pressing the button on Explore device, you can set markers in your code using explorepy.Explore.set_marker function. However, this function must be called from a different thread than the parsing thread. Please not that marker codes between 0 and 7 are reserved for hardware related markers. You can use any other (integer) code for your marker from 8 to 65535. To see an example usage of this function look at this script