Usage¶
Command Line Interface¶
Command structure:
explorepy <command> [args]
You can get help for a specific command by explorepy <command> -h. For example to get help about visualize command, run explorepy visualize -h will result to:
Usage: explorepy visualize [OPTIONS]
Visualizing signal in a browser-based dashboard
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-nf, --notchfreq [50|60] Frequency of notch filter.
-lf, --lowfreq FLOAT Low cutoff frequency of bandpass/highpass filter.
-hf, --highfreq FLOAT High cutoff frequency of bandpass/lowpass filter.
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Note
Explorepy allows users to use either pybluez or Explorepy’s SDK as the Bluetooth interface (in Windows and Ubuntu,
the default BT backend is pybluez and in MacOS, the default BT backend is SDK).
Available Commands¶
find-device Scans for nearby Mentalab Explore devices. Prints out Name and MAC address of the found devices.
- Options:
- -bt, –bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface -h, –help Show this message and exit.
Note
On Windows, this function prints all paired devices.
acquire:
Connect to a device with selected name or address. Only one input is necessary.
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
record-data
Connects to a device and records ExG and orientation data into two separate files. Note that in CSV mode there will be an extra file for the marker events. In EDF mode, the data is actually recorded in BDF+ format (in 24-bit resolution).:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-f, --filename PATH Name of the file. [required]
-ow, --overwrite Overwrite existing file
-d, --duration <integer> Recording duration in seconds
--edf Write in EDF file (default type)
--csv Write in csv file
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Note
If the sampling rate or channel mask has been changed during the recording, Explorepy will create a new EDF/CSV file for ExG data with the given file name plus the time the setting has changed.
Note
To load EDF files, you can use pyedflib or mne (file extension may need to change to bdf manually for mne) in python.
EEGLAB’s BIOSIG plugin has problem with some EDF files currently (see this issue). A precompiled MATLAB code (mexSLOAD.mex) from BIOSIG can be downloaded from this link. The documentaion can be found in this link.
Note
As the environmental factors such as temperature may affect the sampling rate of the ADC, we recommend to compute the sampling rate of the recorded data. In case of deviations, the signal must be resampled to correct drifts. The timestamps in the csv/edf file can be used to compute the resampling factor.
push2lsl Streams data to Lab Streaming Layer (LSL).:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-d, --duration <integer> Streaming duration in seconds
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
bin2csv Takes a Binary file and converts it to three CSV files (ExG, orientation and marker files):
Options:
-f, --filename PATH Name of (and path to) the binary file. [required]
-ow, --overwrite Overwrite existing file
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Note
For devices with firmware version 2.1.1 and lower, Explorepy v0.5.0 has to be used to convert binary files.
Note
If the sampling rate or channel mask has been changed during the recording, Explorepy will create a new CSV file for ExG data with the given file name plus the time the setting has changed.
bin2edf Takes a Binary file and converts it to two EDF files (ExG and orientation - markers will be written in ExG file). The data is actually recorded in BDF+ format (in 24-bit resolution).:
Options:
-f, --filename PATH Name of (and path to) the binary file. [required]
-ow, --overwrite Overwrite existing file
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Note
For devices with firmware version 2.1.1 and lower, explorepy v0.5.0 has to be used to convert binary files.
Note
To load EDF files, you can use pyedflib or mne (file extension may need to change to bdf manually for mne) in python.
EEGLAB’s BIOSIG plugin has problem with some EDF files currently (see this issue). A precompiled MATLAB code (mexSLOAD.mex) from BIOSIG can be downloaded from this link. The documentaion can be found in this link.
Note
If the sampling rate or channel mask has been changed during the recording, Explorepy will create a new EDF file for ExG data with the given file name plus the time the setting has changed.
visualize Visualizes real-time data in a browser-based dashboard. Currently, Chrome is the supported and recommended browser. The visualization in IE and Edge might be very slow, and is not recommended.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-nf, --notchfreq [50|60] Frequency of notch filter.
-lf, --lowfreq FLOAT Low cutoff frequency of bandpass/highpass filter.
-hf, --highfreq FLOAT High cutoff frequency of bandpass/lowpass filter.
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
impedance Visualizes the electrode impedances in a browser dashboard. Currently, Chrome is the supported browser.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Note
Impedance value shown for each electrode is the sum of impedances of ground electrode and corresponding ExG electrode.
Note
The accuracy of measured impedances are subject to environmental conditions such as noise and temperature.
calibrate-orn Calibrate the orientation module of the specified device. After running this module, calibration parameters will be stored in the configuration file of Explorepy. If the orientation module is calibrated, Explorepy computes the physical orientation (degree and rotation axis). Currently, the physical orientation data is not visualized in the dashboard and it is only accessible in python scripts in data packets.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-ow, --overwrite Overwrite existing file
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
format-memory This command formats the memory of the specified Explore device.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
set-sampling-rate This command sets the sampling rate of ExG on the specified Explore device. Acceptable values for sampling rates are 250, 500 or 1000. The default sampling rate of the device is 250 Hz. Please note that 1000 Hz sampling rate is in beta phase.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-sr, --sampling-rate [250|500|1000]
Sampling rate of ExG channels, it can be 250
or 500 [required]
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
set-channels Using this command, you can enable/disable a set of ExG channels of the device. An integer number is required for the channel mask, where the binary representation of it shows the mask (eg. 15 for 00001111, to enable 4 channels of an 8-ch device).:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-m, --channel-mask INTEGER RANGE
Channel mask, it should be an integer
between 1 and 255, the binary representation
will be interpreted as mask. [required]
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
disable-module Using this command, you can disable a module of Explore device. Orientation, environment and ExG modules can be disabled with this command.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-m, --module TEXT Module name to be disabled, options: ORN, ENV, EXG
[required]
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
enable-module If you have already disabled a module of Explore device, you can enable it with this command.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-m, --module TEXT Module name to be enabled, options: ORN, ENV, EXG
[required]
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
soft-reset This command does a soft reset of the device. All the settings (e.g. sampling rate, channel mask) return to the default values.:
Options:
-a, --address TEXT Explore device's MAC address
-n, --name TEXT Name of the device
-bt, --bluetooth [sdk|pybluez] Select the Bluetooth interface
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Example commands:¶
Data acquisition: explorepy acquire -n Explore_XXXX # Put your device Bluetooth name
Record data: explorepy record-data -n Explore_XXXX -f test_file --edf -ow
Push data to lsl: explorepy push2lsl -n Explore_XXXX
Convert a binary file to csv: explorepy bin2csv -f input_file.BIN
Convert a binary file to EDF and overwrite if files exist already: explorepy bin2edf -f input_file.BIN -ow
Visualize in real-time: explorepy visualize -n Explore_XXXX -lf .5 -hf 40 -nf 50
Impedance measurement: explorepy impedance -n Explore_XXXX
Format the memory: explorepy format-memory -n Explore_XXXX
Set the sampling rate: explorepy set-sampling-rate -n Explore_XXXX -sr 500
Set the channel mask: explorepy set-channels -n Explore_XXXX -m 15
To see the full list of commands explorepy -h.
Python project¶
To use explorepy in a python project:
import explorepy
Note
Since explorepy is using multithreading for data streaming, running python scripts in some consoles such as Ipython’s or Spyder’s consoles may lead to strange behaviours.
Initialization¶
Before starting a session, make sure your device is paired to your computer. The device will be shown under the following name: Explore_XXXX, with the last 4 characters being the last 4 hex numbers of the devices MAC address.
Make sure to initialize the Bluetooth connection before streaming using the following lines:
explore = explorepy.Explore()
explore.connect(device_name="Explore_XXXX") # Put your device Bluetooth name
Alternatively you can use the device’s MAC address:
explore.connect(mac_address="XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX")
If the device is not found, you will receive an error.
Explorepy allows users to use either pybluez or Explorepy’s SDK as the Bluetooth interface (in Windows and Ubuntu, the default BT backend is pybluez and in MacOS, the default BT backend is SDK). To change the BT interface, use the following code.
explorepy.set_bt_interface('sdk')
To set the BT interface back to the SDK:
explorepy.set_bt_interface('sdk')
Note
Many MacOS users have reported problems during installation of pybluez, hence only Explorepy’s SDK is supported for MacOS.
Streaming¶
After connecting to the device you are able to stream data and print the data in the console.:
explore.acquire()
Recording¶
You can record data in realtime to EDF (BDF+) or CSV files:
explore.record_data(file_name='test', duration=120, file_type='csv')
This will record data in three separate files “test_ExG.csv”, “test_ORN.csv” and “test_marker.csv” which contain ExG, orientation data (accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer) and event markers respectively. The duration of the recording can be specified (in seconds). If you want to overwrite already existing files, change the line above:
explore.record_data(file_name='test', do_overwrite=True, file_type='csv', duration=120)
Note
To load EDF files, you can use pyedflib or mne (file extension may need to change to bdf manually for mne) in python.
EEGLAB’s BIOSIG plugin has problem with some EDF files currently (see this issue). A precompiled MATLAB code (mexSLOAD.mex) from BIOSIG can be downloaded from this link. The documentaion can be found in this link.
Note
As the environmental factors such as temperature may affect the sampling rate of the ADC, we recommend to compute the sampling rate of the recorded data. In case of deviations, the signal must be resampled to correct drifts. The timestamps in the csv/edf file can be used to compute the resampling factor.
Visualization¶
It is possible to visualize data in real-time in a browser-based dashboard by the following code. Currently, Chrome is the supported browser. The visualization in IE and Edge might be very slow:
explore.visualize(bp_freq=(1, 30), notch_freq=50)
Where bp_freq and notch_freq determine cut-off frequencies of bandpass/lowpass/highpass filter and frequency of notch filter (either 50 or 60) respectively.
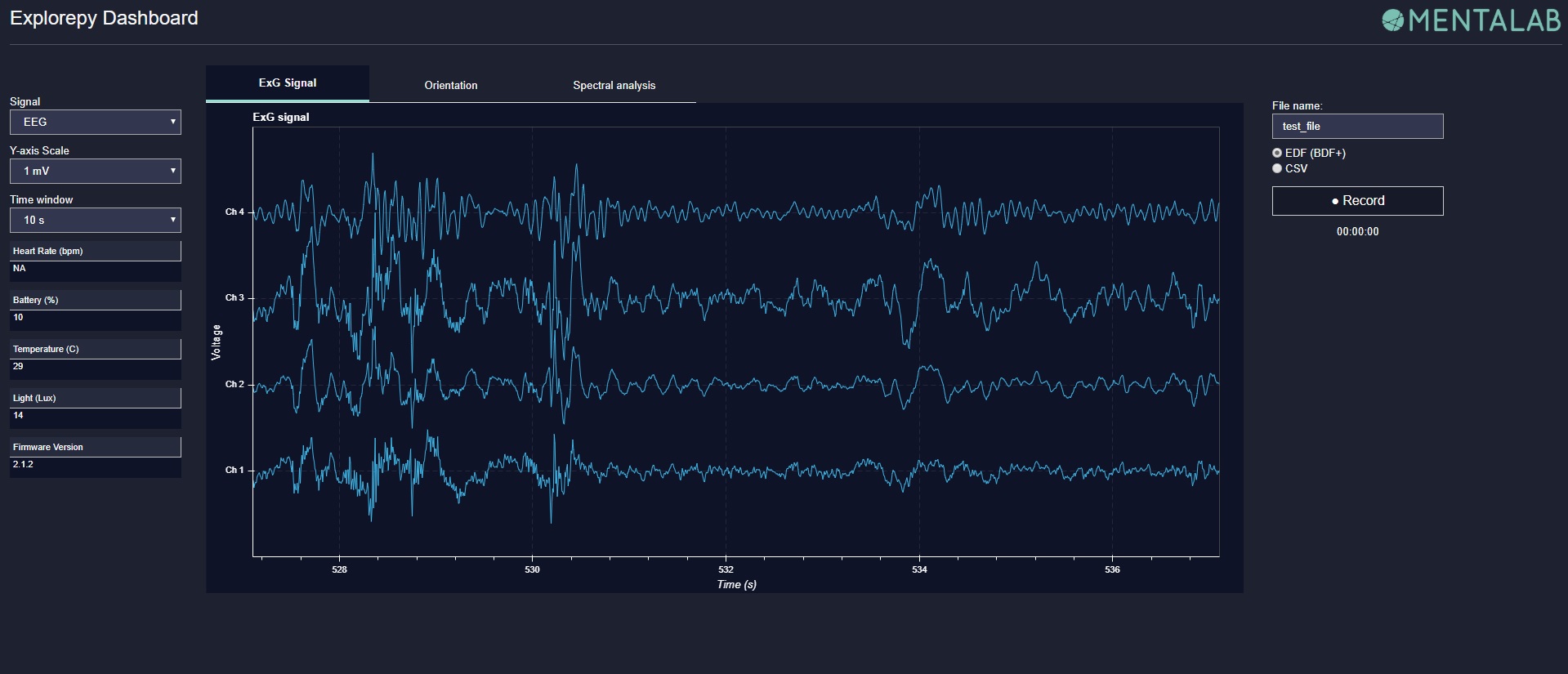
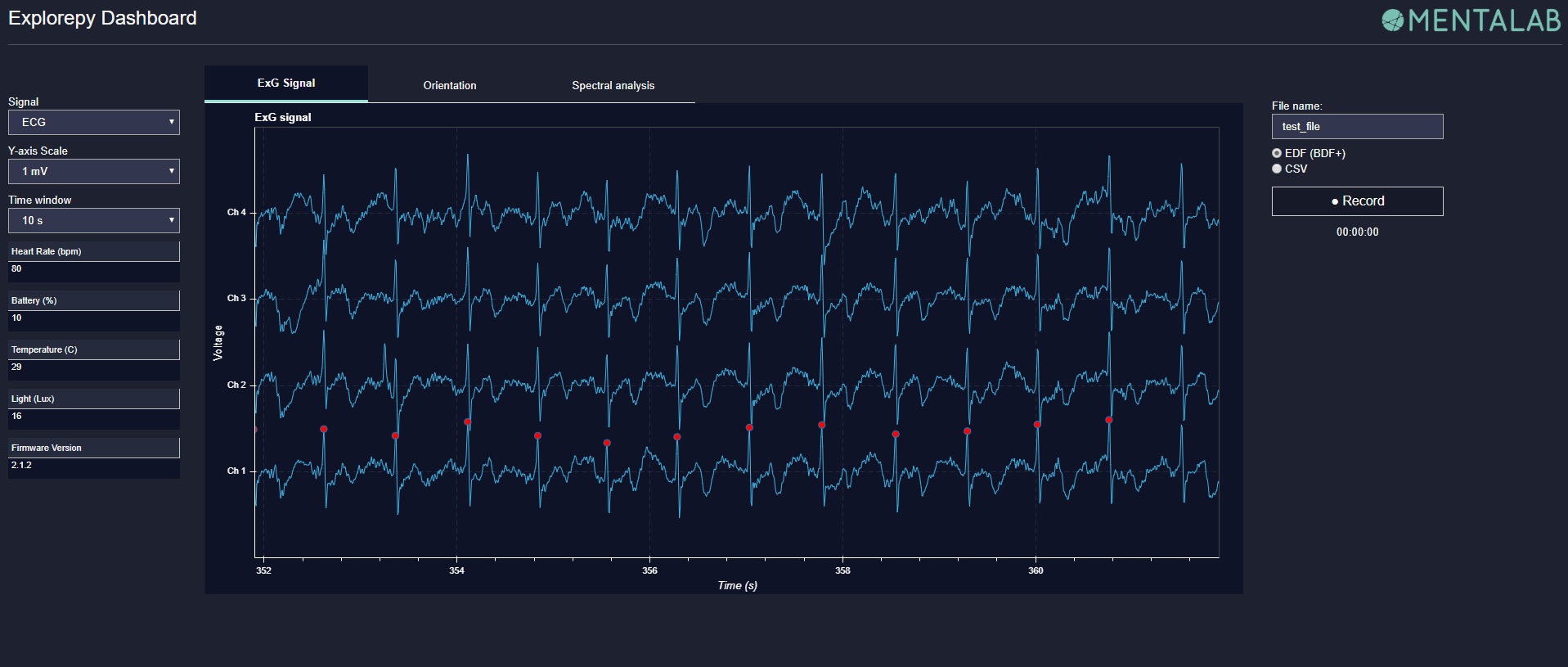
In the dashboard, you can set the signal visualization mode to EEG or ECG. EEG mode provides the spectral analysis plot of the signal. In ECG mode, the heartbeats are detected and heart rate is calculated from the RR-intervals.
EEG:
ECG with heart beat detection:
Impedance measurement¶
To measure electrodes impedances:
explore.measure_imp()
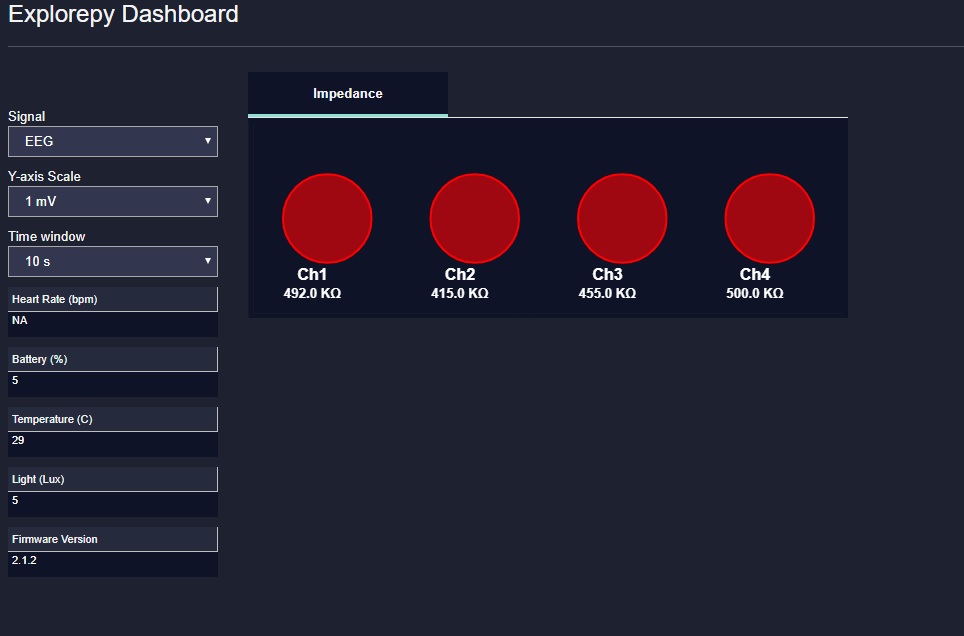
Note
Impedance value shown for each electrode is the sum of impedances of ground electrode and corresponding ExG electrode. This can make the impedances appear higher than they actually are. Make sure your ground is well prepared, when facing issues in getting to low impedances.
Note
The accuracy of measured impedances are subject to environmental conditions such as noise and temperature. Therefore, this works best at regular room temperatures (~15-25 °C).
Labstreaminglayer (lsl)¶
You can push data directly to LSL using the following line:
explore.push2lsl()
With this, you can stream data from other software such as OpenVibe or other programming languages such as MATLAB, Java, C++ and so on. (See labstreaminglayer, OpenVibe documentations for details). This function creates three LSL streams for ExG, Orientation and markers. In case of a disconnect (device loses connection), the program will try to reconnect automatically.
Converter¶
It is also possible to extract BIN files from the device via USB. To convert these to CSV, you can use the function bin2csv, which takes your desired BIN file and converts it to 2 CSV files (one for orientation, the other one for ExG data). A Bluetooth connection is not needed for this.
explore.convert_bin(bin_file='Data001.BIN', file_type='csv', do_overwrite=False)
Note
If the sampling rate or channel mask has been changed during the recording, Explorepy will create a new EDF/CSV file for ExG data with the given file name plus the time the setting has changed.
Event markers¶
In addition to the marker event generated by pressing the button on Explore device, you can set markers in your code using the explorepy.Explore.set_marker function. However, this function must be called from a different thread than the parsing thread. Please not that marker codes between 0 and 7 are reserved for hardware related markers. You can use any other (integer) code for your marker from 8 to 65535. To see an example usage of this function look at this script
Device configuration¶
Using methods of Explore class, the device settings can be changed.
Explore’s sampling rate can be changed to 250, 500 or 1000Hz (default sampling rate is 250Hz).
explore.set_sampling_rate(sampling_rate=500)
Format memory:
explore.format_memory()
The ExG input channels can be deactivated/activated using set_channels method. The unsigned binary representation
of a channel mask will be used to select channels, e.g. 131=0b01000011 means channels 1,2,8 are active.
explore.set_channels(channel_mask=131)
or alternatively:
explore.set_channels(channel_mask=0b01000011)
Orientation, ExG and environment modules can be disabled/enabled using disable_module/enable_module functions.
explore.disable_module(module_name='ORN')
explore.enable_module(module_name='ENV')
You can reset the device to the default settings by:
explore.reset_soft()